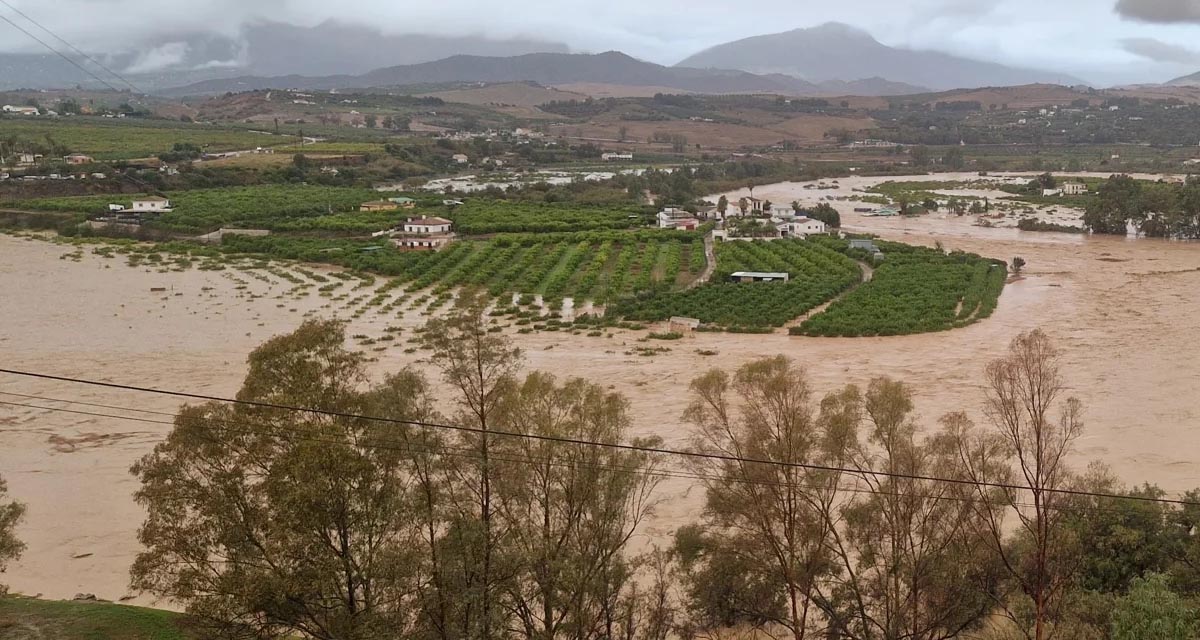
The Mediterranean coastal zone´s combination of multiple severe climate hazards – rising temperatures, water scarcity, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events – makes it a hotspot for highly interconnected climate risks for the ecosystems and societies.
Recent catastrophic floods in the region have caused extreme rain events in coastal watersheds in Spain, Italy, Greece, and Libya, resulting in human losses and severe impacts on the coastal territories.
In this context, the Wetland4Change Euro-MED-funded project (2024-2026) tests and consolidates tools to support regional stakeholders´ preparedness for such extreme climatic events. It seeks to validate transferable solutions based on wetland management (conservation and restoration) for climate adaptation and mitigation purposes, particularly the wetland-based flood regulation within five catchments in the Mediterranean.
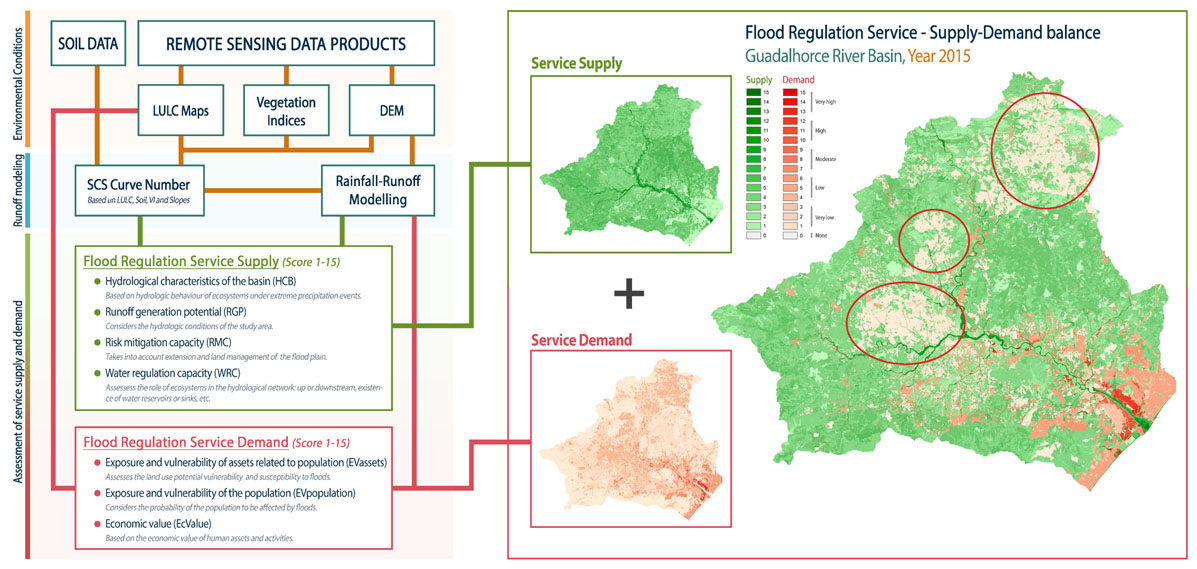 An expert group of Wetland4Change partners, including Tour Du Valat, the University of Valencia, and the University of Málaga, gathered this week to consolidate an assessment methodology that integrates spatial modelling and remote sensing techniques to enhance flood regulation capacity of these ecosystems while securing water demand for public use and economic activities within a catchment.
An expert group of Wetland4Change partners, including Tour Du Valat, the University of Valencia, and the University of Málaga, gathered this week to consolidate an assessment methodology that integrates spatial modelling and remote sensing techniques to enhance flood regulation capacity of these ecosystems while securing water demand for public use and economic activities within a catchment.
In the coming months, the outcomes of this meeting will be implemented at the project´s test sites in Bulgaria, France, Greece, Italy, and Spain, and contribute to a Living Lab event in Oristano, Italy.

Wetlands for change technical meeting participants at the premises of the European Topic Centre for Spatial Analysis and Synthesis (ETC-UMA).



